By Mattia Viale
A couple of years ago I was sitting in a coffee-house in Antwerp and working on my database. A group next to me started a small and informal business meeting which got rather loud. The manager eventually turned to me to apologise for the noise the team was making. While we were talking, he saw my laptop screen that contained a large, multi-coloured Excel file, full of figures and codes. He thought I was an accountant. When told him that I was an early modern historian, his reaction was of amazement and perplexity. What does history have to do with statistical databases?
Quantitative history may indeed seem a strange or even contradictory for many. How is it possible to study a subject, which is considered par excellence qualitative, through the schematised and rigid ‘cage’ of a database?
The answer lies in the fact that, in reality, quantitative approach is much less rigid than one may at first think. It is, in fact, sometimes the only way to organise large quantities of historical data, in order to arrive at conclusions beyond examples and case-studies.
The results are impressive especially when the sources are suitable for a quantitative treatment (and potentially all sources are suitable) and the analysis is based on an adequate system. The potentials of quantitative approach in history can be illustrated well by studies that rely on post-mortem inventories as their main source. The extensive exploitation of these documents through quantitative approach has been fundamental over the years when historians have, among other issues, investigated levels of wealth and analysed trends in inequality in the past, or reconstructed the steps that led to the creation of the modern model of consumption. It would be difficult to address such complex topics comprehensively using just a dozen of documents.
Refashioning the Renaissance project follows this fruitful line of research, and combines the study of hundreds of post-mortem inventories with qualitative research, in order to shed light on the transformation and the adaptation of fashion, as well as on the meaning and the changing cultural attitudes to dress. Yet, the question remains, how to study the quantitative point of view in practice? In the following, I will introduce the steps that lead from the ‘raw material’ to the ‘finished product’, that is, from the archival document to the final outcomes of a database.

The first page of the inventory of Serafino, the blacksmith, who died in Siena in 1603. Archivio di Stato di Siena, Curia del Placito, Tutele e Inventari, 275, c. 42r.
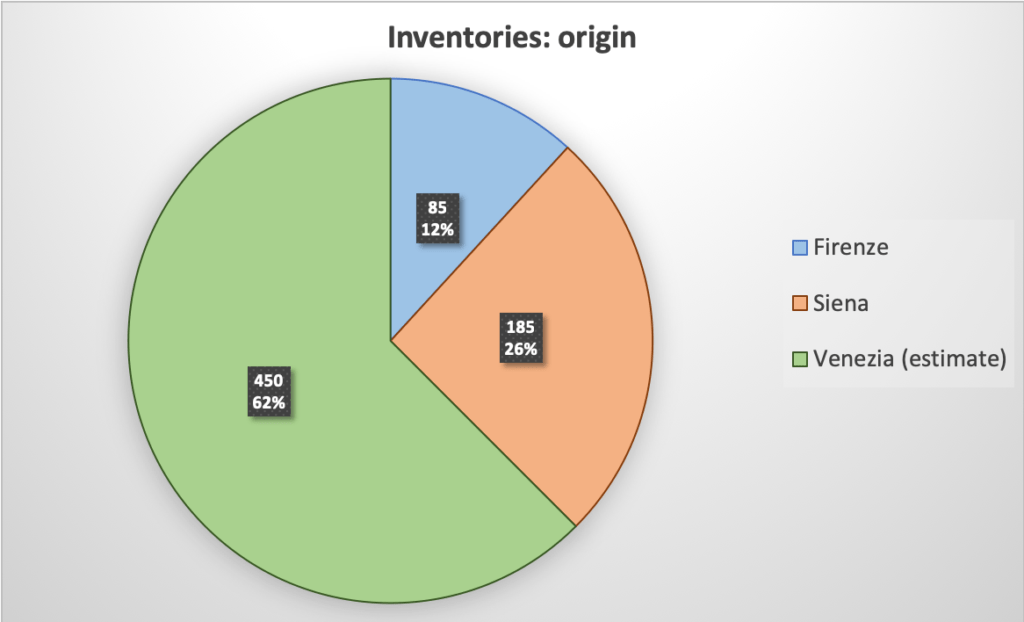
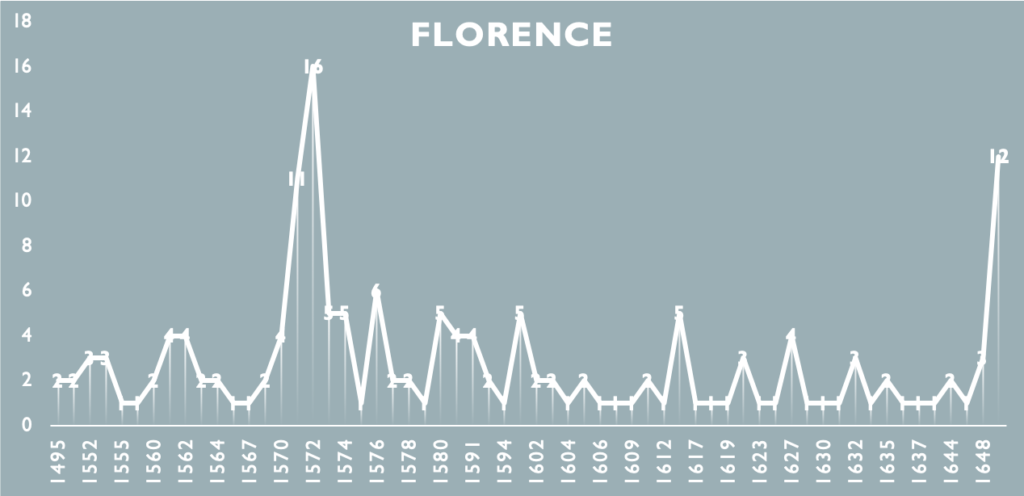
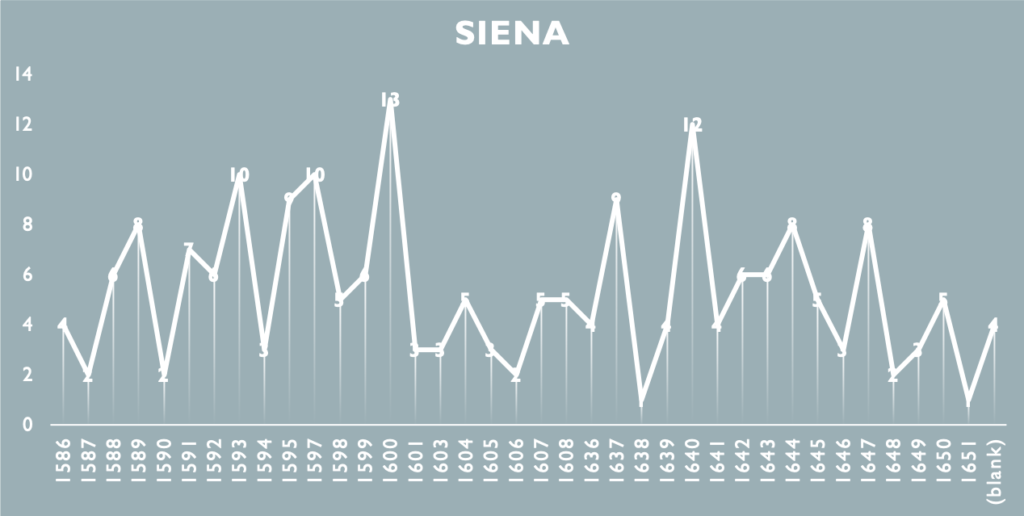
The first step is obviously to collect the historical sources. This involves going to the archive, looking for the right documents at indexes and catalogues, and requesting all the folders needed. This takes time. In addition, transcribing the documents by hand, one by one, and taking pictures of all the documents requires a lot of patience. To give a sense of the scale of the work, the Refashioning the Renaissance project has identified and gathered over 1500 post-mortem inventories, belonging to craftsmen and small shopkeepers who died in urban centres of Siena, Florence, Venice or in the Scandinavian town of Elsinore between 1550 and 1650.
Once the documents have been identified, collected, reproduced and transcribed, we can move on to the second stage: to transpose the data from the sources into the database. This work can be done in two different ways. The first option is to work in a source oriented way, i.e. to record all the information in the document word by word (verbatim) on the database, and thus to preserve both the original content as well as the structure of the document. Alternatively, the researcher can choose to work in a method oriented way, inserting only those parts of the information in the database that he or she has decided in advance are most interesting and relevant to the study. Both approaches are equally valid, and the choice between the two depends only on the characteristics of the study. Since the Refashioning the Renaissance focuses on a precise and circumscribed research topic, and there are a large number of sources to process, the most appropriate option was to conduct a method oriented study.
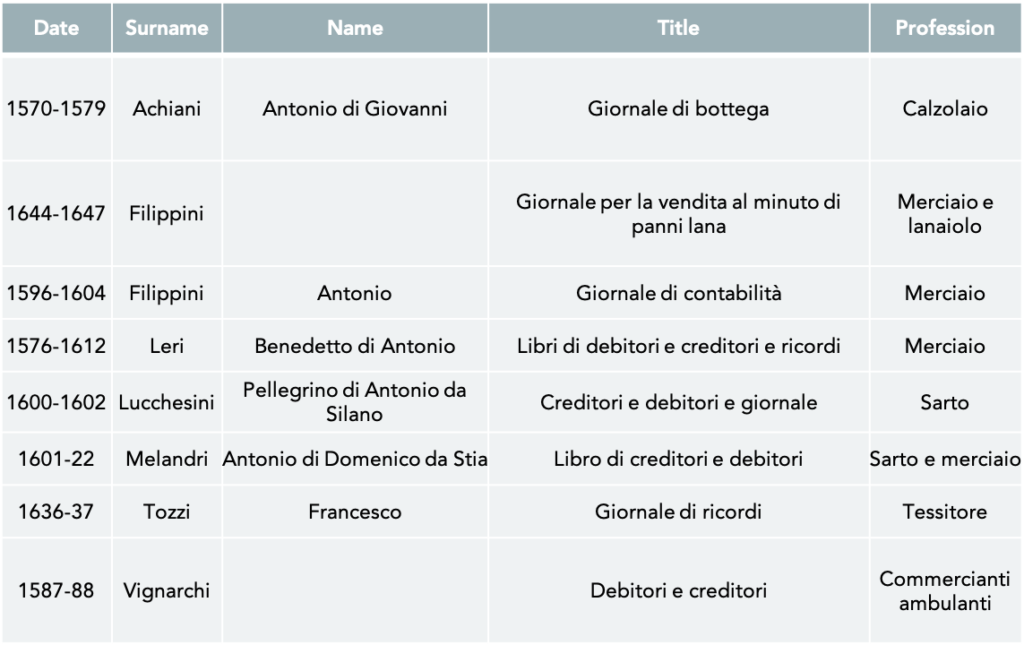
Once the decision has been made about the categories of object that one wants to focus on, one can start the actual data entry – or at least its first part. In this phase, the collected documents are analysed page by page, line by line. The data recorded at this stage is relatively basic, but it provides important technical information, for example, about the archival location of the document as well as about the individuals whose documents we are dealing with, such as the owner’s name, profession, place of residence, and the date of the document. This is followed by a faithful transcription of the description of the objects that were recorded in the document.
The work at this stage is laborious and takes time. Just for Florence and Siena, for example, we recorded more than 14000 textile objects, clothing articles and fashion accessories that belonged to artisans and shopkeepers, including a wide range of hats, gloves, skirts, aprons and shirts of different colour and kind. This means that we filled 14000 lines of the Excel sheet. The task is often complicated by the fact that the handwriting in the document might be bad or the document is in poor condition.
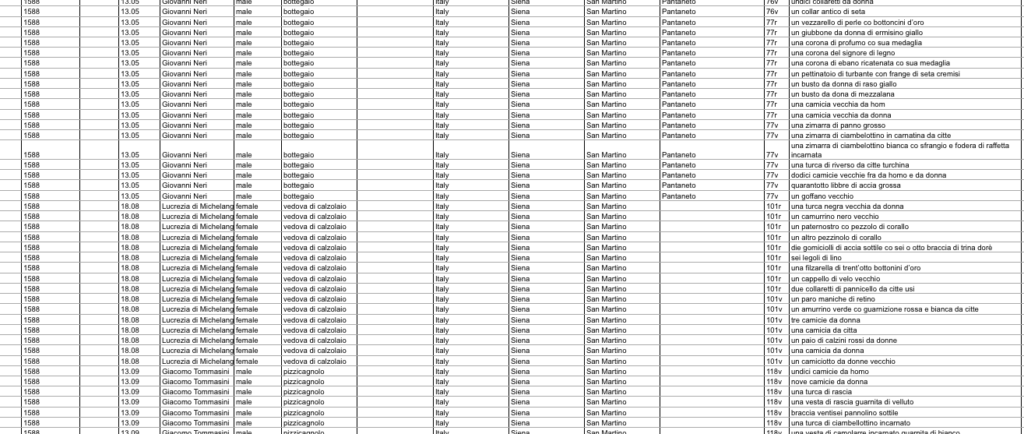
The Refashioning the Renaissance database after the first step of data entry.
Nevertheless, the research is exciting. Post-mortem inventories are indeed interesting documents, since they allow us virtually to enter the homes that people of the past lived in. We can visit all the spaces of the house -the main bedroom which was usually reserved for the householder and his wife, and the hall that was used to throw parties during important occasions such as weddings and childbirths. We can visualise and appreciate the paintings that were hanging on their walls, observe the decoration which embellished beds and wardrobes, and even open every drawer or trunk that contained their clothing, from modest shirts and skirts worn for work, to elaborate silk aprons that were embellished with trims and embroidery. Once the basic data entry is completed, we extract the data. This means that all the descriptions of object are broken up and organised in many small units of information. We record in separate columns, for example, what type of object of clothing we are dealing it, its colour, material and finishing, and what the condition of the item is (whether it was new, used, old).
After this, we can move on to the third step, the data standardisation. The variety of objects, colours, and materials in our database is so wide that it would be difficult to analyse the data without a consistent system of categorisation. Therefore, it is necessary to catalogue the information by identifying broad, homogeneous, and consistent categories. To provide an example, when we look at the colour of the objects, the various shades of red (rosso, pavonazzo, cremisi, and so on) are grouped under the same umbrella category called ‘red’. The same goes, for instance, for the huge variety of fabrics made of wool such as saie, rascie, panni, and saiette which are catalogued under the ‘wool’ label. The standardisation is perhaps one of the most important and delicate phases of the entire database creation process. In fact, the categories created cannot be too large (the results risk to be too vague and therefore not informative), nor too narrow (the risk here is to offer only many small impressions, without showing general trends). The data standardisation also makes it possible to check the various entries for mistakes and correct errors, as well as, crucially, to translate the information in English (or eventually in any other language), making the database usable by a larger number of people.

Different shades of red. A.S.L. Archivio Sardini, n. 68/1. Samples of drappi attached to a book, commissioned at the fabbrica of Bartolomeo Talenti, 1771-1784 Catalogue, Arti e mestieri, n. 8.
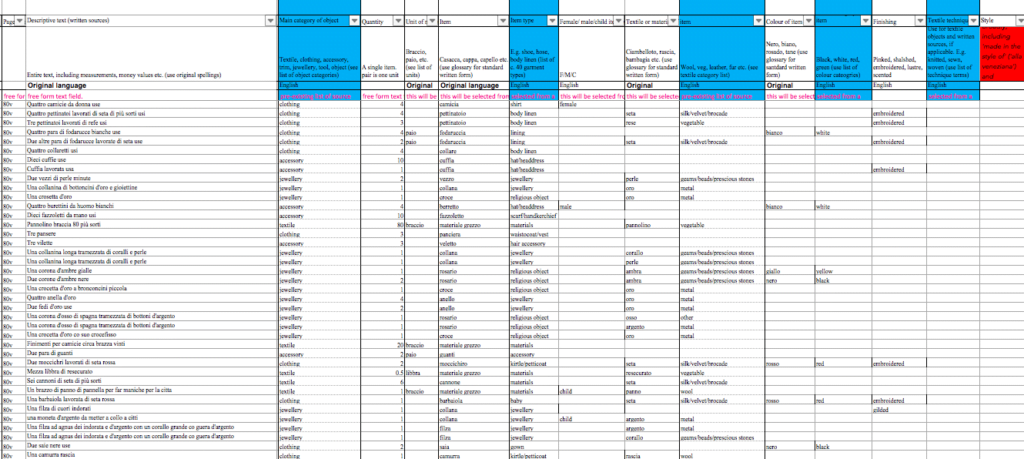
The Refashioning the Renaissance database in its final form.
Once the standardisation phase is finished, the database is in its final form and it is ready to be properly used and tested. The Refashioning the Renaissanceproject has created a dedicated online database in collaboration with Jodie Cox from Wildside, which will be available for everyone in the future. This allows one to do searches on the clothing, accessories and jewellery that our artisans and small shopkeepers owned, including their materials, colours, cut and condition of the articles, as well as how these were decorated and combined with other garments. All entries can be seen in both processed from as well as in the original documents, or organised in charts and tables according to years, geographical location, clothing types, colours and so forth.
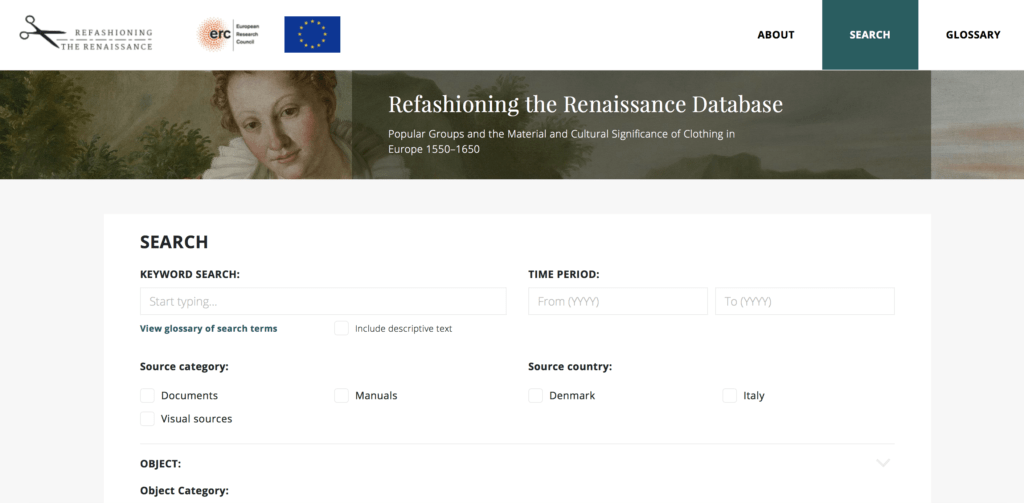
Finished database, which will be open for public in the future.
A database, despite its granitic appearance, is in fact an organism capable of evolving in a thousand different ways, moulding itself to the needs of the researcher. This extreme flexibility is probably the greatest strength of this kind of quantitative approach and also the reason why it is particularly suitable for the analysis of historical issues.
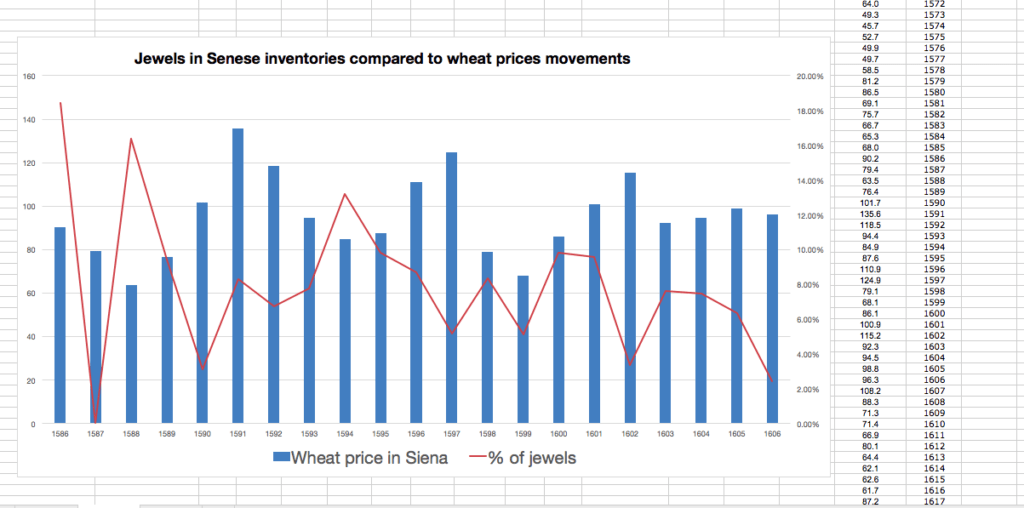
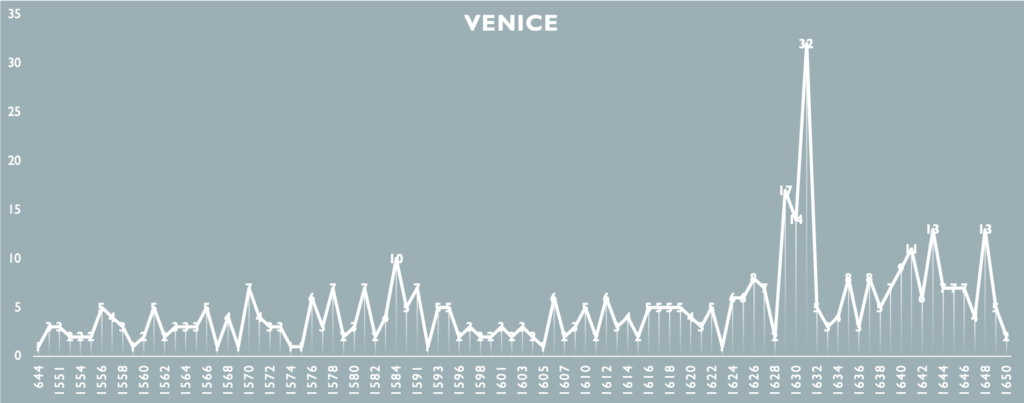
Some preliminary tests using the database.
Mattia worked with us for three months, assisting Stefania Montemezzo in the data standardisation and transcriptions for the database. Read more about the database on Stefania’s project page.